
Israel | Iran conflict analysis
Wednesday 24 April 2024
This situation report summarises the key events of the April 2024 clashes between Iran and Israel, along with the munitions and delivery platforms employed.
Analysts at Fenix Insight have been monitoring the conflict events taking place between Iran and Israel over the past weeks. Having collated this information, we have produced a situation update outlining the key dates, event records, munitions and platforms with links to our OSINT system, METIS. Data is captured from April 1 to April 23, 2024.
Current conflict situation in the Middle East
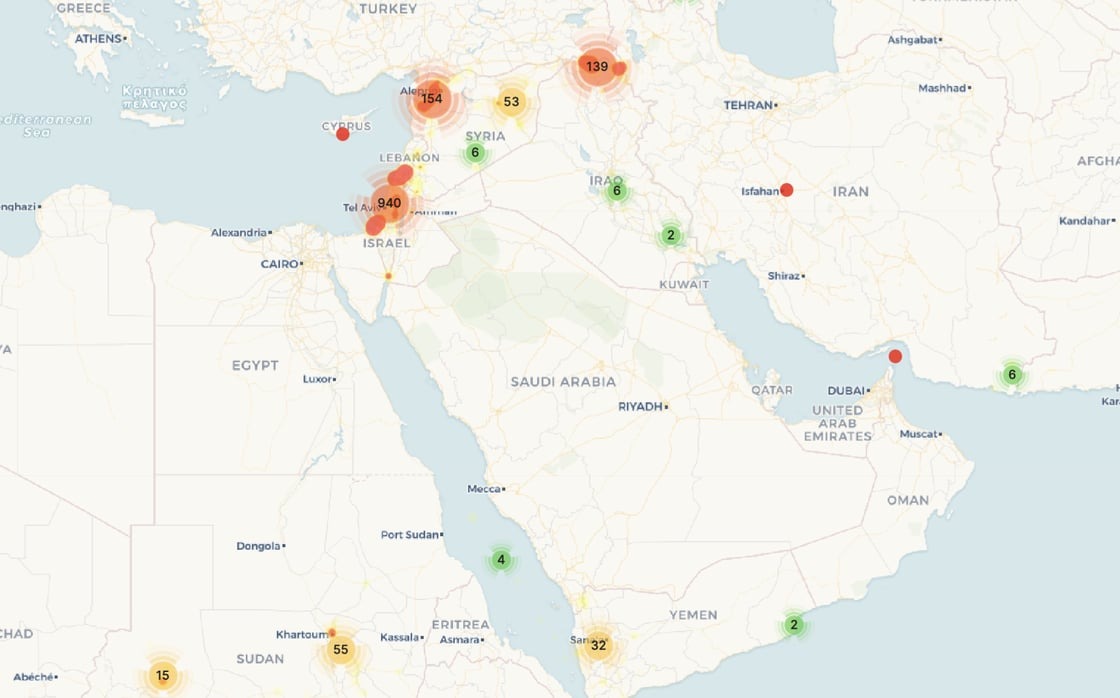
Conflict events captured in METIS since April 1 2024.
APRIL 1st 2024: Israel strikes Iranian consulate
On April 1st 2024, a building within the Iranian consulate in Syria was struck, reportedly killing 16 people. Among these casualties were seven high ranking Iranian Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) personnel, including the Chief of the General Staff of IRGC in Syria and Lebanon. It is not known exactly what munitions were used in this strike, however they were deployed from an F-35I Adir aircraft. The F-35I Adir is the Israeli variant of the Lockheed Martin F-35 Lightning II.
US fighter jet |
Single-seat, supersonic, multirole fighter aircraft manufactured by Lockheed Martin. |
 |
April 12-15: Retaliation against the Israeli strike on Iran
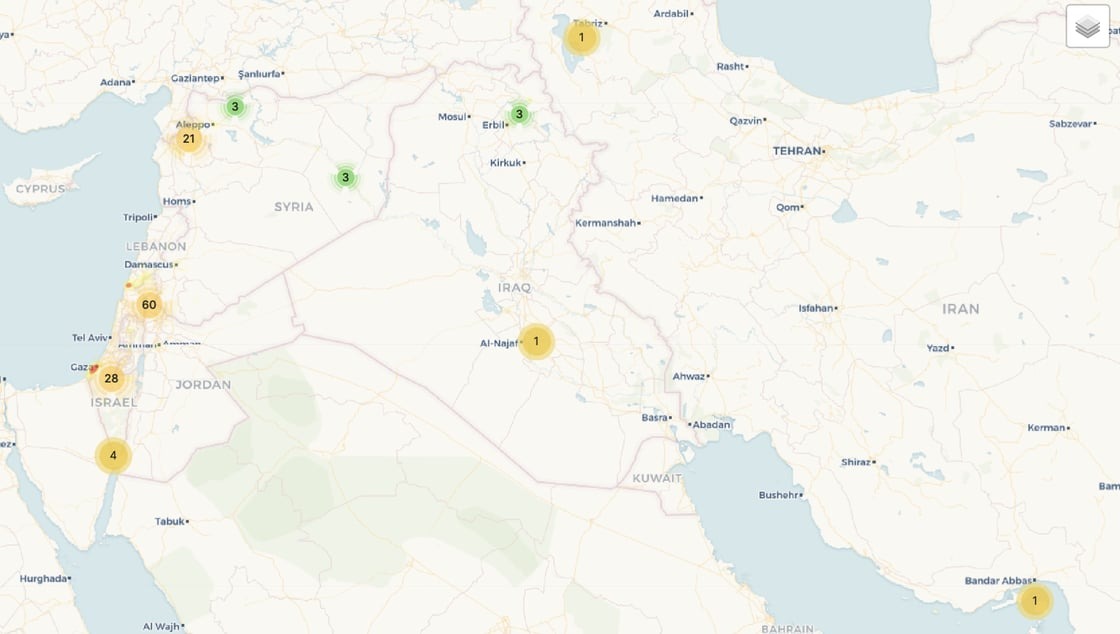
Conflict events captured in METIS during Iran and Hezbollah retaliatory strikes on Israel. April 12-15.
A large volume of 122 mm 9M22 unguided high explosive rockets were launched by Hezbollah in Lebanon against targets in northern Israel on April 12. While this is a common occurrence, the scale of the attacks were larger than the ongoing sub-threshold conflict. It is believed that these were part of the co-ordinated retaliation by Iran, with the low cost rockets forcing Israel to use air defence interceptor missiles to reduce their availability for the upcoming strikes on April 13.
The 9M22 and key events showing attacks on Israel are shown below:
Russian rocket |
Soviet-era-developed, high-explosive fragmentation warhead-equipped rocket. |
 |
On April 13, following the attacks by Hezbollah, Iran retaliated for the consulate strike by launching an estimated 300 one way attack drones, cruise missiles and ballistic missiles, against various targets in Israel:
The attack was split into waves, with the first being ~170 one way attack drones and the second being ~120 ballistic and ~30 cruise missiles.
During this period, Houthi rebel forces in Yemen also launched UAV platforms and missiles into Israel. These were intercepted by Israeli air-defence systems.
The co-ordination of these strikes being intended to overwhelm Israeli air defences.
Platforms and munitions used during retaliation strikes
One-Way Attack Drones
It has been confirmed that Shahed-136 one way attack drones were utilised by Iran, however it is possible that other Shahed variants were deployed. The Shahed-136 is an Iranian HESA, cropped delta-wing, propeller-driven one way attack drone that is 3.5 m long, with a 40-50 kg nose-mounted warhead, and has a maximum velocity and range of approximately 170 kph and 2000 km respectively. It is commonly fielded by Iran and its proxies, with a nickname of the ‘lawnmower’ due to the sound made by its four-cylinder 50 hp engine.
As with the earlier Hezbollah strikes on the 12th, it is believed that the Shahed-136 drones were utilised to exhaust Israeli air defences prior to the strikes by the cruise and ballistic missiles.
Iranian drone series |
Series of one way attack drones. Originally developed by Iran but can be manufactured by other countries. |
 |
Iranian drone |
One-way attack drone. Length of 3.5 m and range of 2000 km. |
 |
Iranian missiles
The missiles launched by Iran included the Fateh 110 series and Ghadr 110 series, such as the Kheibar Shekan, Dezful, Zolfaghar, Fateh 313 and Emad ballistic missiles, along with the Paveh/Quds-351 cruise missile. These missiles were launched to reportedly reach their targets shortly after the one way attack drone, under the assumption the air defences would have been overwhelmed.
Israeli air-defence systems
The Israeli Defence Force (IDF) initiated Operation Iron Shield to defend themselves from the incoming threats, along with support from allies. The IDFs integrated air defence system was put into action, with both ground based systems and air platforms engaging the one way attack drones, cruise missiles and ballistic missiles.
Israeli ground-based systems included:
Short-range Iron Dome, launching Tamir Inteceptors | Medium range David's Sling, launching Stunner Inteceptors | Medium range US-made Patriot Missile systems |
 |  |  |
Israeli air platforms include:
F-35I Adir | F-15IA Strike Eagle |
US / Israeli fighter jet | US / Israeli fighter jet |
Based off the F-35 Lightning II. Multirole stealth jet fighter aircraft. | Twin-engine, supersonic, multirole, fixed-wing strike fighter aircraft. |
 |  |
Allied air-defence platforms include:
F-15E Strike Eagle | Arleigh Burke Class Destroyer | Eurofighter typhoon |
 |  |  |
US Navy Arleigh Burke Class destroyers, USS Arleigh Burke and USS Carney, which fired SM-2 and SM-3 missiles. This being the first combat use of the SM-3 ballistic missile interceptor.
April 19: Israel strikes Iran
Key events below:
Munitions encountered:
Israeli missile system | Russian missile series |
Air-to-surface missile thought to be based on the Black Sparrow ALBM platform. | Soviet-era-developed Surface-to-Air missile air-defence system. |
 |  |
Initial reports were that one way attack drones had been deployed in Israel’s strike on Iran, however a crashed Israeli missile in Iraq indicated differently. This missile was found on April 19th and appears to be a derivative of one of the Israeli Sparrow-family of air-launched ballistic missile targets. The Sparrow family, which emulate short- to medium-range ballistic missiles, were developed by Rafael and include: the Black Sparrow; the Blue Sparrow; and the Silver Sparrow. The crashed missile is believed to be Rafael's ROCKS stand-off air-launched ballistic missile, which is thought to be based on the Black Sparrow.
It is believed this is a limited response by Israel to avoid escalation in the region, while still highlighting its capabilities. There was reportedly little to no engagement by Iranian air defences, highlighting vulnerabilities. While Israel did not strike the Natanz nuclear facility directly, it has shown the capability to do so, with both Iran and Israel previously threatening each other's nuclear power plants. An attack on any nuclear facility can negatively affect power generation to the country attacked, however this also risks releasing radiation or inducing a partial or full nuclear meltdown.
We hope this comprehensive overview of the developing situation in the Middle East has been useful.
Please do not hesitate to reach out to us if you would like to discuss the contents of this Sit Rep, or if you have any questions regarding METIS.
Fenix Insight welcome your use of our data, visualisations, analysis, and other information, but always with proper attribution and a link back to our website. Please read our Attribution Policy for further information.
Source Information
Where our site contains links to other sites and resources provided by third parties, these links are provided for your information only. We have no control over the contents of those sites or resources, and accept no responsibility for them or for any loss or damage that may arise from your use of them. If you find a broken link or a link directing you to website material you feel is unsuitable, please contact us. If you have any queries about information accessed through links, you are advised to check directly with the organisation concerned.

Tenuous ceasefires: Cross‑border conflicts of 2025
8 Jan 2026

Risks posed by Explosive Remnants of War in Gaza and the associated clearance challenges
26 Nov 2025

Mexican cartels using drones to expand and enhance their arsenals
16 Oct 2025

Rising use of one-way attack FPV drones by state and non-state actors
10 Sept 2025








